Introduction
In today’s fast-paced, tech-driven world, education has become more accessible, flexible, and diverse than ever before. As digital tools continue to shape every aspect of our lives, the way we learn is also evolving. While traditional classroom learning remains a cornerstone of education, online learning has rapidly risen as a powerful and convenient alternative.
From virtual classrooms to self-paced apps, online education now plays a central role in how people of all ages acquire knowledge and skills. This shift is not about replacing traditional methods, but about expanding the possibilities for learners everywhere.
The purpose of this article is to compare online and traditional learning approaches, highlighting their unique strengths and challenges. Whether you’re a student, working professional, or lifelong learner, this guide will help you determine which method—or mix of both—best fits your goals, lifestyle, and learning preferences.
Defining the Two Learning Methods
2.1 What is Online Learning?
Online learning refers to education delivered through digital platforms, allowing learners to access content anytime and from virtually anywhere. It has gained significant popularity for its flexibility, affordability, and wide accessibility.
Online learning can take many forms, including:
- Video lectures
- Interactive quizzes and assignments
- Virtual classrooms and live sessions
- Mobile learning apps and self-paced courses
Common platforms and formats include:
- Coursera – University-level courses with certification options
- Udemy – Skill-based learning for professionals and hobbyists
- Duolingo – Language learning through gamified lessons
- Google Classroom – A digital tool for organizing assignments and communication in school settings
This method is ideal for remote learners, working adults, and anyone seeking a more flexible, on-demand approach to education.
2.2 What is Classroom Learning?
Classroom learning, also known as traditional or face-to-face education, takes place in physical settings such as schools, universities, or training centers. It is led by an instructor and typically follows a structured schedule.
Common features of classroom learning include:
- In-person lectures and discussions
- Group activities and collaborative projects
- Hands-on experiences in labs, studios, or workshops
- Immediate interaction and feedback from teachers and peers
This method is especially effective for learners who benefit from routine, social interaction, and hands-on instruction in a controlled environment.
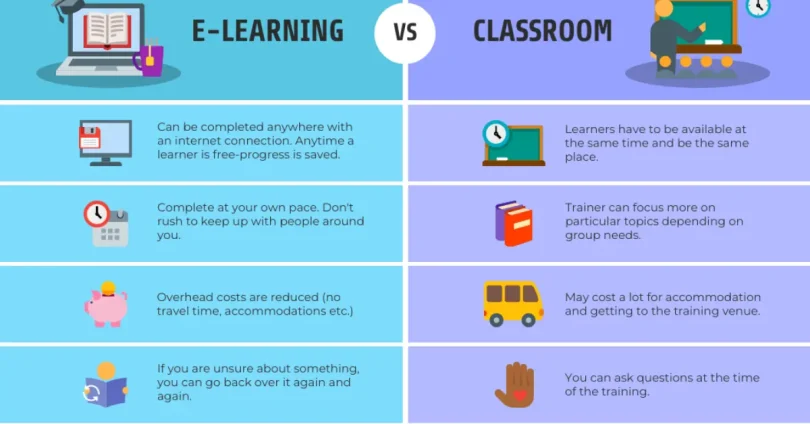
Online Learning vs. Classroom Learning: Key Comparison Factors
To help learners choose the right educational path, it’s important to evaluate both online learning and classroom learning across several key dimensions:
3.1 Flexibility and Accessibility
- Online Learning: Offers the ability to learn anytime and anywhere, making it ideal for people with irregular schedules, remote learners, or working professionals.
- Classroom Learning: Requires fixed schedules and physical attendance, which can be limiting for those balancing work, family, or other responsibilities.
3.2 Cost and Affordability
- Online Learning: Often more affordable, with many free or low-cost options. Learners can avoid costs related to commuting, housing, and physical materials.
- Classroom Learning: Typically involves higher tuition fees, along with additional expenses like transportation, accommodation, and textbooks.
3.3 Interaction and Communication
- Online Learning: Interaction happens through forums, discussion boards, and messaging tools. While convenient, it may feel impersonal for some.
- Classroom Learning: Encourages real-time, face-to-face discussions and social engagement, fostering deeper emotional and collaborative connections.
3.4 Self-Motivation and Discipline
- Online Learning: Requires strong self-discipline and motivation, as students often manage their own schedule and progress.
- Classroom Learning: Provides external structure and accountability, with teachers and peers encouraging participation and consistency.
3.5 Learning Pace and Style
- Online Learning: Allows learners to progress at their own pace, which is beneficial for those who prefer to move faster or revisit complex topics.
- Classroom Learning: Follows a standardized pace, which may not suit every learner. However, it can benefit those who thrive in structured environments.
3.6 Technology and Resource Requirements
- Online Learning: Requires reliable internet access, digital devices, and basic technical skills.
- Classroom Learning: Generally requires fewer tech resources, relying on in-person interaction and traditional materials.
3.7 Practical Learning and Labs
- Online Learning: May lack the ability to provide real-time, hands-on practice, especially for subjects that require physical experimentation or teamwork.
- Classroom Learning: Well-suited for practical work like lab sessions, group projects, and hands-on training, offering a more immersive experience.
3.8 Feedback and Assessment
- Online Learning: Feedback can be automated or delayed, especially in self-paced courses. Learners may have to wait for instructor responses.
- Classroom Learning: Allows for immediate feedback and real-time clarification from instructors, which can enhance understanding and retention.
Pros and Cons

4.1 Pros and Cons of Online Learning
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Learn anytime, anywhere at your own pace
- Accessibility: Ideal for remote learners or those with time constraints
- Affordability: Many free or low-cost courses available
- Variety: Wide range of topics, platforms, and learning formats
- Self-Paced Learning: Great for learners who want to control their speed and depth
Challenges:
- Requires Self-Discipline: Lack of structure can lead to procrastination
- Limited Social Interaction: Less face-to-face engagement with peers and instructors
- Tech Dependence: Requires internet access, devices, and basic tech skills
- Hands-On Learning Limitations: Difficult to replicate labs or practical experiences online
- Delayed Feedback: Support and grading may not be immediate
you may also like to read these posts:
Best Business Computers in 2025: Performance & Reliability
Powerful & Compact: Best Portable Mini PCs for Work
Exploring Various Budgeting Strategies to Take Control of Your Money
The Process of Using Online Tools for Effective Learning
Online or In-Person? A Side-by-Side Look at Modern Education
4.2 Pros and Cons of Classroom Learning
Advantages:
- Structured Environment: Fixed schedules help build routine and accountability
- Direct Interaction: Immediate access to instructors and peer collaboration
- Effective for Hands-On Learning: Ideal for labs, workshops, and group projects
- Immediate Feedback: Real-time clarification and guidance
- Social Experience: Encourages teamwork, communication, and relationship-building
Limitations:
- Less Flexibility: Attendance and timing are rigid
- Higher Costs: Includes tuition, travel, housing, and material expenses
- Geographic Restrictions: Limited to local institutions and commuting distances
- Standardized Pace: May not suit all learning styles or speeds
- Disruption Risks: Learning can be affected by closures, illness, or travel issues
Use Cases: Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between online and classroom learning depends largely on your personal circumstances, goals, and preferred learning style. Below are common scenarios that can help guide your decision:
When Online Learning is Ideal
- Working Professionals
If you’re balancing a job and want to upskill, earn a certificate, or change careers, online courses offer the flexibility to learn on your own schedule. - Remote Learners
For those living in rural areas or far from educational institutions, online platforms eliminate the need for travel and provide access to quality education. - Lifelong Learners with Flexible Goals
Whether you’re learning for personal growth, exploring hobbies, or staying mentally active, online learning allows you to pick subjects and progress at your own pace. - People with Irregular Schedules
Shift workers, caregivers, or travelers benefit from the 24/7 availability of online courses and mobile-friendly learning apps.
When Classroom Learning is Better
- School and College Students
Younger learners often benefit from structured routines, direct supervision, and the social development that comes from in-person education. - Learners Who Need Personal Guidance
If you thrive on face-to-face interaction, real-time support, and personalized feedback, classroom settings provide immediate access to instructors and peers. - Subjects with Labs or Hands-On Practice
Disciplines like science, engineering, medicine, or the arts often require physical labs, equipment, or collaborative projects that are best experienced in person. - Learners Struggling with Self-Motivation
If you find it hard to stay on track independently, the accountability built into classroom environments may help you succeed more effectively.
Blended Learning: The Best of Both Worlds
Blended learning, also known as hybrid learning, combines the strengths of both online and classroom education to create a more flexible, effective learning experience. This model integrates digital tools and in-person instruction, allowing students to benefit from the advantages of each method.
What is Blended Learning?
In a blended learning environment, students might attend traditional classes while also engaging with online content such as video lectures, quizzes, or discussion forums. This approach enables learners to access material anytime outside the classroom, while still receiving direct support and social interaction during face-to-face sessions.
How Are Students and Institutions Combining Both Methods?
Many schools, colleges, and training centers are adopting blended models to enhance learning outcomes and adapt to diverse student needs. For example, a course might include weekly in-person labs or seminars complemented by online lectures and assignments. This combination helps accommodate different learning styles and schedules, encourages active participation, and allows for personalized pacing.
The Future of Education: Digital and In-Person Integration
As technology advances, blended learning is expected to become the standard approach in education. It offers a balanced solution—leveraging the accessibility and flexibility of online learning while preserving the engagement, collaboration, and hands-on experiences of traditional classrooms. This integrated model promises to make education more inclusive, adaptable, and effective for learners worldwide.
Faqs:
Which is more effective: online learning or classroom learning?
Effectiveness depends on the learner’s style, discipline, and the subject matter. Classroom learning offers more direct interaction, while online learning provides flexibility and accessibility.
Are online learning certificates recognized by employers?
Many online courses from reputable platforms offer certificates that employers value, especially if they are from accredited institutions or well-known companies.
Can children benefit from online learning?
Yes, but younger children often need more supervision and interactive support, which is easier in a classroom setting. Online learning can be a great supplement.
How can online learners stay motivated without in-person classes?
Setting clear goals, following a schedule, joining online study groups, and using interactive learning tools can help maintain motivation.
Is classroom learning becoming obsolete with the rise of online education?
No, classroom learning still plays a crucial role, especially for subjects requiring hands-on practice and social interaction. Many institutions now use a blended approach combining both.
Conclusion:
Both online learning and classroom learning offer unique benefits and challenges, making them suitable for different learners and situations. Online learning excels in flexibility, accessibility, and affordability, making it ideal for busy professionals and self-motivated students. Meanwhile, classroom learning provides structured environments, immediate feedback, and valuable face-to-face interaction, which can be essential for subjects requiring hands-on practice or social engagement.