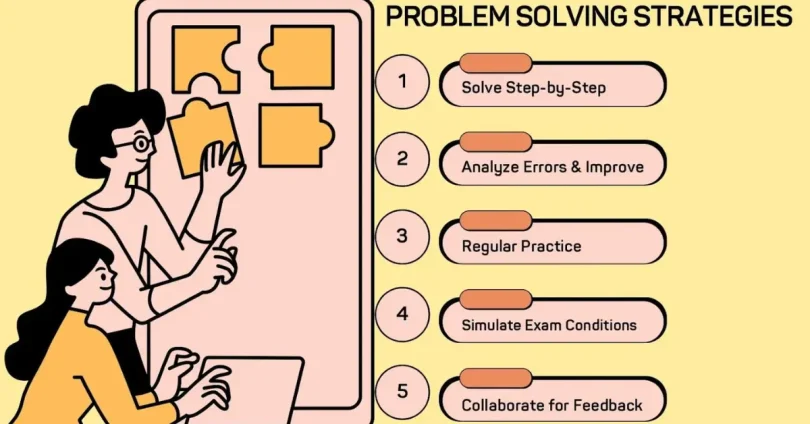
Introduction
Problem-solving skills are essential for navigating the challenges we face in both personal and professional life. Whether it’s overcoming obstacles at work, making important decisions, or handling everyday situations, the ability to effectively solve problems can greatly improve outcomes and reduce stress.
Problem-solving is a multi-faceted skillset that involves critical thinking, creativity, decision-making, and the ability to analyze situations from different perspectives. It’s not just about finding any solution, but finding the best one.
The purpose of this post is to categorize and explain the different types of problem-solving skills, helping you understand how to develop and apply them effectively in various contexts.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?

Problem-solving skills refer to the ability to identify challenges, analyze situations, generate effective solutions, and implement those solutions to overcome obstacles. These skills enable individuals to approach difficulties methodically and confidently, turning problems into opportunities for growth and improvement.
Key Components of Problem-Solving Skills:
- Identifying the Problem: Recognizing and clearly defining the issue that needs resolution.
- Analyzing the Problem: Gathering relevant information, understanding causes, and breaking down complex issues into manageable parts.
- Generating Solutions: Brainstorming multiple possible approaches or alternatives to address the problem.
- Decision-Making: Evaluating the pros and cons of each solution and selecting the most suitable option.
- Implementation: Putting the chosen solution into action and monitoring its effectiveness to ensure the problem is resolved.
Mastering these components allows for effective, efficient, and creative problem-solving in various aspects of life.
Categorizing Problem-Solving Skills
3.1 Analytical Skills
Analytical skills involve breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts. This includes logical reasoning and data analysis to understand the root cause of an issue.
Real-world example: A data analyst examining sales trends to identify why revenue dropped in a particular quarter.
3.2 Creative Thinking
Creative thinking means approaching problems with innovation and originality. It encourages thinking outside the box and brainstorming unconventional solutions.
Case study: A marketing team devising a unique campaign that stands out in a crowded marketplace.
3.3 Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the objective evaluation of information and arguments. It involves questioning assumptions, identifying biases, and applying logic to make well-informed judgments.
Example: A manager assessing multiple vendor proposals by critically evaluating costs and benefits rather than relying on intuition.
3.4 Decision-Making Skills
Decision-making is the process of selecting the best solution among alternatives. It requires prioritization and commitment. Techniques like pros and cons lists or decision trees help clarify choices.
Example: Choosing the right software platform by comparing features, costs, and user reviews.
3.5 Research Skills
Research skills focus on gathering relevant information effectively. This involves using proper data collection methods and validating sources to ensure accuracy.
Example: A student conducting thorough research using credible academic journals for a thesis.
3.6 Teamwork and Collaboration
Problem-solving often benefits from diverse perspectives. Effective communication and consensus-building within teams lead to more comprehensive solutions.
Example: A cross-functional team collaboratively developing a new product feature by integrating feedback from different departments.
3.7 Adaptability and Flexibility
Adaptability is the ability to adjust to changing circumstances and handle uncertainty or unexpected obstacles. Being flexible ensures continued progress despite challenges.
Real-life scenario: A project manager revising timelines and strategies after sudden budget cuts.
3.8 Persistence and Resilience
Persistence involves continuing to work through difficulties, learning from mistakes, and maintaining motivation. Resilience helps bounce back after failures.
Example: An entrepreneur refining their business model after multiple setbacks until achieving success.
How to Develop Each Type of Problem-Solving Skill

4.1 Developing Analytical Skills
- Practice breaking down complex problems into smaller parts by mapping out causes and effects.
- Work on puzzles and logic games like Sudoku or brainteasers to improve logical reasoning.
- Analyze case studies or data sets relevant to your field to sharpen data interpretation.
- Exercise: Take a recent problem you faced and list all contributing factors and possible consequences.
4.2 Building Creative Thinking
- Use brainstorming sessions without judgment to generate as many ideas as possible.
- Try techniques like mind mapping to explore connections between concepts.
- Challenge assumptions by asking “What if?” questions to open up new possibilities.
- Exercise: Set a daily or weekly “idea challenge” where you come up with alternative solutions for a simple task.
4.3 Improving Critical Thinking
- Question assumptions by asking for evidence and alternative viewpoints.
- Engage in debates or discussions to practice evaluating different perspectives objectively.
- Read critically by analyzing the arguments in articles or books, identifying biases and logical fallacies.
- Exercise: After reading an opinion piece, write down the main argument and at least two counterarguments.
4.4 Enhancing Decision-Making Skills
- Use decision-making tools like pros and cons lists, decision trees, or SWOT analysis to organize options.
- Practice prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance.
- Reflect on past decisions to understand what worked and what didn’t.
- Exercise: For your next decision, create a pros and cons list and evaluate outcomes afterward.
4.5 Strengthening Research Skills
- Learn to identify credible sources such as peer-reviewed journals, official websites, and expert opinions.
- Practice effective note-taking and summarizing to organize information.
- Use multiple sources to cross-verify facts and avoid misinformation.
- Exercise: Pick a topic and research it using at least three different reputable sources, then summarize your findings.
4.6 Enhancing Teamwork and Collaboration
- Improve communication skills to share ideas clearly and listen actively.
- Engage in group projects or team sports to experience diverse viewpoints and cooperation.
- Practice conflict resolution techniques such as negotiation and compromise.
- Exercise: Participate in a team activity and focus on facilitating open dialogue and shared decision-making.
4.7 Cultivating Adaptability and Resilience
- Embrace change by seeking new experiences and stepping out of your comfort zone.
- Develop a growth mindset by viewing failures as learning opportunities.
- Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness and problem-focused coping.
- Exercise: Reflect on a recent setback and write down what you learned and how you can adjust moving forward.
you may also like to read these posts:
Comparing Group Study and Self Study: Benefits and Best Uses
Best Business Computers in 2025: Performance & Reliability
Powerful & Compact: Best Portable Mini PCs for Work
Exploring Various Budgeting Strategies to Take Control of Your Money
Understanding Different Types of Problem-Solving Skills
Application of Problem-Solving Skills in Different Contexts
5.1 Workplace Challenges
Problem-solving is crucial in the workplace to address issues such as project delays, resource constraints, and team conflicts. Employees use analytical skills to identify bottlenecks, creative thinking to develop innovative solutions, and decision-making to select the best course of action. Leaders rely on problem-solving to guide teams, manage risks, and drive organizational success.
Example: Resolving a sudden supply chain disruption by quickly analyzing alternatives and coordinating with vendors.
5.2 Academic Problem-Solving
Students regularly apply problem-solving skills to understand complex concepts, complete assignments, and prepare for exams. Research skills help gather information, while critical thinking aids in evaluating sources and arguments. Collaboration is often necessary during group projects to combine knowledge and perspectives.
Example: Developing a research paper by formulating a clear thesis, conducting thorough research, and presenting logical arguments.
5.3 Everyday Life Situations
From managing personal finances to resolving conflicts at home, problem-solving helps individuals navigate daily challenges. Adaptability and resilience are key when dealing with unexpected situations, while decision-making skills guide choices like budgeting or time management.
Example: Planning a family vacation by comparing costs, schedules, and preferences to find the best option.
5.4 Leadership and Management
Effective leaders use problem-solving to set strategic goals, motivate teams, and overcome organizational challenges. They apply teamwork and collaboration skills to build consensus and adaptability to respond to market changes. Persistence ensures they stay focused on long-term objectives despite setbacks.
Example: Leading a company through a market downturn by innovating product offerings and restructuring operations.
Faqs:
What are the most important problem-solving skills to develop?
The key skills include analytical thinking, creativity, critical thinking, decision-making, research, teamwork, adaptability, and persistence. Developing a mix of these will help you tackle a variety of challenges effectively.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills quickly?
Start by practicing specific exercises like puzzles or brainstorming sessions, seek feedback, reflect on your approach to problems, and expose yourself to diverse situations that require problem-solving
Are problem-solving skills only useful at work?
No, problem-solving skills are valuable in all areas of life—academics, everyday personal situations, leadership roles, and social interactions. They help you make better decisions and handle challenges more efficiently.
How does teamwork enhance problem-solving?
Teamwork brings together diverse perspectives, ideas, and expertise, leading to more comprehensive solutions. Collaboration also fosters better communication and shared responsibility for outcomes.
Can problem-solving skills be taught, or are they innate?
While some people may have a natural aptitude, problem-solving skills can definitely be learned and improved through practice, education, and real-life experience.
Conclusion:
Problem-solving is a vital skill that combines various abilities, from analytical thinking to creativity, teamwork, and resilience. Understanding the different types of problem-solving skills helps you approach challenges more effectively and confidently. By developing and practicing these diverse skills, you can become a versatile problem solver capable of handling any situation—whether in your career, studies, or everyday life. Remember, great problem solvers aren’t born; they’re made through continuous learning and experience.