Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving job market, having the right set of skills is essential for career development. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to climb the professional ladder, your skills determine how effectively you can perform your job, adapt to new challenges, and collaborate with others. Employers no longer focus solely on qualifications or experience—they’re increasingly interested in the unique blend of abilities that candidates bring to the table.
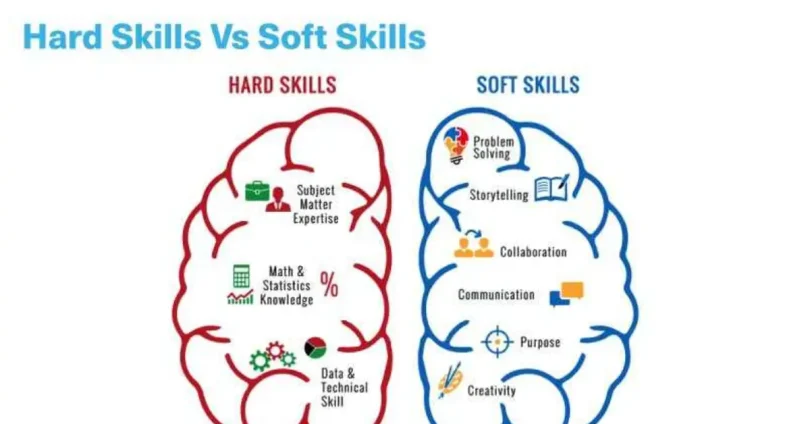
Skills generally fall into two main categories: soft skills and hard skills. Hard skills are the technical, job-specific abilities you’ve gained through education, training, or experience—such as coding, data analysis, or using specialized software. In contrast, soft skills are personal attributes that influence how you interact with others and handle workplace situations. These include communication, problem-solving, teamwork, and adaptability.
The purpose of this blog is to explore the differences between soft skills and hard skills, highlight their significance in professional success, and help you understand how to develop both to thrive in your career.
What Are Hard Skills?
Hard skills are the specific, teachable abilities or knowledge sets that you can measure and quantify. These skills are often gained through formal education, professional training, or hands-on experience, and they are directly related to the technical aspects of a job. Unlike soft skills, which are more personality-driven, hard skills are objective and can be tested or certified.
How Hard Skills Are Acquired
Hard skills are typically learned through:
- Formal education (e.g., university degrees, vocational schools)
- Professional training programs
- Certifications and licenses
- On-the-job experience
- Online courses and self-study
For example, a graphic designer might learn to use Adobe Creative Suite through a design course, while an accountant may acquire knowledge in tax regulations and financial reporting through a degree program or certification.
Relevance in Job Descriptions and Resumes
Hard skills are often the first things employers look for in job applicants. They are clearly listed in job descriptions, such as:
- “Proficient in Microsoft Excel”
- “Must be fluent in Spanish”
- “Experience with JavaScript and Python required”
On a resume, hard skills help you stand out and demonstrate your technical competence. Including relevant hard skills tailored to the job you’re applying for increases your chances of being noticed by recruiters and applicant tracking systems (ATS).
Common Examples of Hard Skills Across Different Industries
Here are some examples of hard skills, categorized by industry:
- Technology & IT
- Programming languages (e.g., Python, Java, C++)
- Database management
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud computing (e.g., AWS, Azure)
- Healthcare
- Patient care techniques
- Electronic medical records (EMR) management
- Phlebotomy
- Medical coding and billing
- Finance & Accounting
- Financial analysis
- QuickBooks or SAP proficiency
- Budgeting and forecasting
- Tax preparation
- Marketing & Communications
- SEO/SEM
- Social media analytics
- Graphic design
- Email marketing platforms (e.g., Mailchimp)
- Construction & Engineering
- CAD software
- Blueprint reading
- Safety compliance
- Project management tools
Mastering hard skills is essential for meeting the technical demands of a role—but it’s only half of the equation when it comes to workplace success. The other half lies in your ability to work with people, adapt to change, and lead effectively, which brings us to soft skills.
What Are Soft Skills?

Soft skills are the personal attributes, habits, and social abilities that influence how you interact with others and navigate your work environment. Unlike hard skills, soft skills are not easily measured or taught in a traditional classroom—they are often developed through experience, self-reflection, and real-world interactions. These skills shape how effectively you communicate, collaborate, lead, and adapt in professional settings.
How Soft Skills Are Developed
Soft skills are typically developed over time through:
- Life experiences such as volunteering, group projects, or part-time jobs
- Practice in real-world scenarios, including workplace interactions and teamwork
- Feedback and reflection, helping you understand your strengths and areas for growth
- Self-awareness and emotional intelligence, which play a critical role in recognizing and managing your own behavior and responses
Unlike hard skills, which can often be learned through a course or certification, soft skills require conscious effort and consistent application in everyday situations.
Their Role in Team Dynamics and Workplace Culture
Soft skills are essential for creating a positive and productive workplace. They help employees:
- Build trust and rapport with colleagues
- Resolve conflicts effectively
- Adapt to changes and challenges
- Contribute to a healthy team environment
- Lead and motivate others
In fact, many employers say that soft skills are just as important—if not more so—than hard skills when it comes to long-term success. A technically skilled employee who lacks communication or teamwork skills may struggle to thrive in a collaborative environment.
Common Examples of Soft Skills
Here are some of the most valued soft skills across industries:
- Communication – Active listening, clear writing, public speaking
- Teamwork – Collaborating effectively, supporting colleagues
- Problem-Solving – Thinking critically, finding creative solutions
- Adaptability – Embracing change, learning quickly
- Time Management – Prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines
- Leadership – Inspiring others, making decisions, delegating
- Emotional Intelligence – Managing emotions, empathizing with others
- Conflict Resolution – Handling disagreements calmly and constructively
While hard skills may get your foot in the door, soft skills often determine how far you’ll go. The ability to balance both is what makes professionals truly effective in any workplace.
Key Differences Between Soft Skills and Hard Skills
Understanding the distinction between soft skills and hard skills is essential for personal and professional growth. While both are critical for success in the workplace, they differ in several key areas, including their nature, how they’re acquired, measured, and evaluated during the hiring process.
Here’s a clear side-by-side comparison:
| Aspect | Hard Skills | Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Skills | Technical, job-specific, and teachable | Interpersonal, behavioral, and personality-driven |
| Method of Acquisition | Learned through formal education, training, certifications | Developed through experience, self-awareness, and practice |
| How They Are Measured | Easily tested or assessed through exams, portfolios, or demonstrations | Difficult to quantify; evaluated through behavior and feedback |
| Relevance in Hiring | Often used as the baseline for job qualification | Increasingly valued for teamwork, leadership, and culture fit |
| Examples | Coding, accounting, foreign languages, data analysis | Communication, adaptability, problem-solving, empathy |
Examples That Illustrate the Differences
- A software developer needs hard skills like programming in Python and using version control systems. But to succeed in a team setting, they also need soft skills like collaboration and communication.
- A project manager must understand hard skills such as budgeting and project planning tools, but their ability to lead a team, resolve conflicts, and manage stress relies heavily on soft skills.
In short, hard skills help you get the job, but soft skills help you keep it and grow within it. A balance of both is essential for long-term career success.
Why Both Skill Types Matter
In the modern workplace, having just one type of skill—hard or soft—is rarely enough to excel. Both skill sets complement each other and together shape how effectively you perform your job and grow in your career.
Real-World Scenarios Where Both Are Essential
- Example 1: Software Development
A developer may have strong hard skills like coding and debugging, but without soft skills such as teamwork and communication, they might struggle to collaborate with designers, testers, and project managers. Successful projects require both technical expertise and the ability to work well with others. - Example 2: Healthcare
A nurse must have the hard skills to administer medication and monitor patient vitals accurately. However, soft skills like empathy, patience, and clear communication are crucial to provide compassionate care and effectively interact with patients and their families. - Example 3: Sales
A salesperson might be skilled at product knowledge (hard skill), but their ability to listen, build rapport, and negotiate (soft skills) often determines whether they close deals and maintain customer relationships.
you may also like to read these posts:
Powerful & Compact: Best Portable Mini PCs for Work
Exploring Various Budgeting Strategies to Take Control of Your Money
Exploring Digital Learning Platforms: Types and Their Educational Purposes
Understanding the Difference Between Soft Skills and Hard Skills
How Soft Skills Enhance the Application of Hard Skills
Soft skills act as the “glue” that helps apply hard skills effectively. For instance, critical thinking and problem-solving enable professionals to troubleshoot technical issues more creatively and efficiently. Communication skills help present complex information clearly to clients or team members who may not have the same technical background.
Impact on Career Advancement and Job Performance
- Employees with a strong combination of hard and soft skills are often seen as more adaptable and valuable, making them prime candidates for promotions and leadership roles.
- Soft skills like emotional intelligence and conflict resolution improve workplace relationships, reduce misunderstandings, and foster a positive culture, all of which contribute to higher productivity and job satisfaction.
- Mastery of hard skills ensures that employees can perform their core tasks competently, but without soft skills, their ability to influence, motivate, and collaborate is limited.
In summary, both hard and soft skills are essential for not only doing your job well but also for thriving, advancing, and making a meaningful impact in your career.
Industry Perspective
The importance and balance of hard and soft skills can vary widely depending on the industry, but recent trends show an increasing emphasis on soft skills across nearly all sectors.
How Different Industries Prioritize These Skills
- Technology & IT
While hard skills like programming, cybersecurity, and data analysis remain fundamental, tech companies increasingly value soft skills such as teamwork, creativity, and adaptability. Agile work environments demand employees who can communicate effectively and pivot quickly. - Healthcare
Hard skills related to medical knowledge and patient care are non-negotiable. However, soft skills such as empathy, communication, and emotional resilience are critical for patient interaction and teamwork in high-pressure environments. - Finance & Banking
Technical skills like financial modeling and regulatory knowledge are essential. At the same time, soft skills like integrity, negotiation, and client relationship management are vital for building trust and long-term success. - Education
Teachers need strong hard skills in subject matter expertise, but soft skills such as patience, communication, and adaptability are crucial to engage students and manage classrooms effectively. - Manufacturing & Engineering
Technical expertise in machinery, design, or production processes is key. However, collaboration, problem-solving, and leadership skills are important for managing projects and improving efficiency.
Trends in Hiring: Increasing Value of Soft Skills
- According to a 2023 report by LinkedIn, over 90% of hiring managers say soft skills are equally or more important than hard skills in their decision-making process.
- The World Economic Forum highlights that by 2025, skills like critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence will be among the top skills employers look for across industries.
- Many companies are now incorporating behavioral assessments and situational interviews to evaluate candidates’ soft skills alongside technical competencies.
Summary
While hard skills remain crucial for fulfilling job-specific tasks, the growing recognition of soft skills reflects a shift toward valuing adaptability, collaboration, and emotional intelligence in the workplace. Employers increasingly understand that technical expertise paired with strong interpersonal abilities leads to better team performance and overall business success.
How to Develop Hard and Soft Skills
Developing both hard and soft skills is essential for staying competitive and growing in your career. While they require different approaches, continuous improvement in both areas will boost your professional effectiveness and open new opportunities.
Tips for Improving Hard Skills
- Take Courses and Certifications: Enroll in formal training programs, online courses, or workshops relevant to your field. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer a wide range of technical courses and certification programs.
- Practice Regularly: Hands-on experience is key. Apply your knowledge through projects, internships, or freelance work to reinforce learning.
- Stay Updated: Technology and industry standards change rapidly. Follow industry news, join professional groups, and attend conferences or webinars to keep your skills current.
- Use Tools and Software: Become proficient with industry-standard tools and software to stay efficient and competitive.
Tips for Developing Soft Skills
- Self-Reflection: Regularly assess your communication, teamwork, and leadership qualities. Identify areas for improvement and set goals.
- Seek Feedback: Ask colleagues, mentors, or supervisors for constructive feedback on your interpersonal skills and behavior.
- Practice Real-Life Application: Engage in group projects, volunteer opportunities, or leadership roles where you can practice collaboration, conflict resolution, and adaptability.
- Develop Emotional Intelligence: Work on understanding your emotions and others’ perspectives to improve empathy and relationship management.
- Read and Learn: Books, podcasts, and workshops on communication, leadership, and personal development can provide valuable insights and techniques.
Importance of Lifelong Learning
The modern workplace is constantly evolving, making lifelong learning crucial. Embracing a mindset of continuous growth helps you:
- Adapt to new technologies and methodologies
- Enhance both hard and soft skills over time
- Stay relevant and competitive in your career
- Open doors to new roles and responsibilities
In short, developing hard and soft skills is an ongoing journey that requires dedication, curiosity, and openness to feedback. By committing to lifelong learning, you position yourself for long-term success and fulfillment in your professional life.
Balancing Both for Career Success
Why a Balance of Both Skills Is Ideal
Achieving career success requires more than just technical expertise or interpersonal abilities alone—it’s the combination of both hard and soft skills that truly sets professionals apart. Hard skills enable you to perform job-specific tasks effectively, while soft skills help you collaborate, lead, and adapt within the workplace. Together, they enhance your overall performance, make you a valuable team member, and prepare you for leadership roles. Employers increasingly seek candidates who can not only do the work but also fit well into their company culture and navigate challenges smoothly.
How to Highlight Them on Resumes, in Interviews, and on LinkedIn
- On Your Resume:
Include a dedicated Skills section that lists both hard and soft skills relevant to the job. Use specific keywords from the job description. For example, pair “Data Analysis” (hard skill) with “Problem Solving” (soft skill). Use bullet points in your experience section to demonstrate how you applied these skills in real situations. - In Interviews:
Prepare to give concrete examples showcasing both types of skills. Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to describe how you used hard skills to solve a problem and soft skills to collaborate or lead. For instance, explain how you used technical expertise to complete a project and communication skills to coordinate with your team. - On LinkedIn:
Highlight a balanced mix of skills in your profile’s Skills & Endorsements section. Write a summary that reflects both your technical qualifications and your interpersonal strengths. Share posts or articles that demonstrate your expertise and thought leadership in both areas.
Personal Branding Through Skill Presentation
How you present your skills shapes your personal brand. Emphasize your unique combination of hard and soft skills to position yourself as a well-rounded professional. Showcase stories that reflect your problem-solving ability alongside your leadership or teamwork experiences. This balanced narrative helps recruiters and employers see not just what you know, but how you apply it—and why you’d be an asset to their organization.
Ultimately, mastering and presenting both hard and soft skills effectively builds a powerful personal brand that opens doors to greater career opportunities and growth.
Faqs:
What is the main difference between soft skills and hard skills?
Hard skills are technical, teachable abilities specific to a job, while soft skills are interpersonal traits that help you work well with others and adapt to workplace challenges.
Can soft skills be learned, or are they innate?
Soft skills can definitely be developed over time through practice, self-awareness, and real-life experiences.
Which skills do employers value more: soft skills or hard skills?
Both are important. Employers look for hard skills to ensure you can do the job, but soft skills are crucial for teamwork, communication, and leadership.
How can I improve my soft skills?
You can improve soft skills by seeking feedback, practicing effective communication, working in teams, and developing emotional intelligence.
How should I showcase my soft and hard skills on my resume?
Highlight hard skills in a dedicated skills section with specific tools or certifications. Showcase soft skills through examples in your experience and achievements.
Conclusion
In today’s dynamic job market, both soft skills and hard skills are essential for success. While hard skills demonstrate your technical ability to perform specific tasks, soft skills shape how you interact, adapt, and grow within any workplace. Understanding the difference between these skills—and actively developing both—can give you a competitive edge, improve your career prospects, and help you thrive in any professional environment. Strive for a balance, and you’ll be well-equipped to meet the challenges of the modern workplace.