Introduction
The future job market and society are evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by rapid technological advancements, globalization, and shifting economic landscapes. These changes are creating new opportunities and challenges, requiring a workforce that is adaptable, innovative, and equipped with a diverse set of skills.
Preparing students with future-ready skills is more important than ever to ensure they can thrive in this dynamic environment. Beyond technical knowledge, students need critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, and emotional intelligence to navigate complex problems and work effectively with others.
This post aims to highlight the key skills students will need to succeed in the future and explore practical ways they can develop and apply these skills both inside and outside the classroom.
What Are Future Skills?
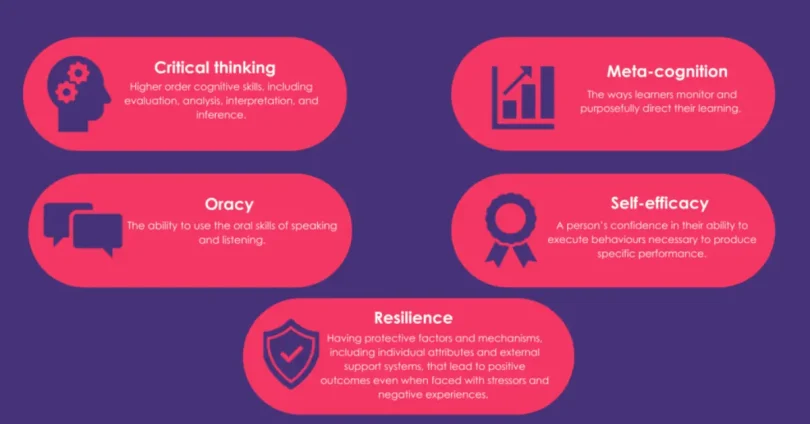
Definition and Explanation
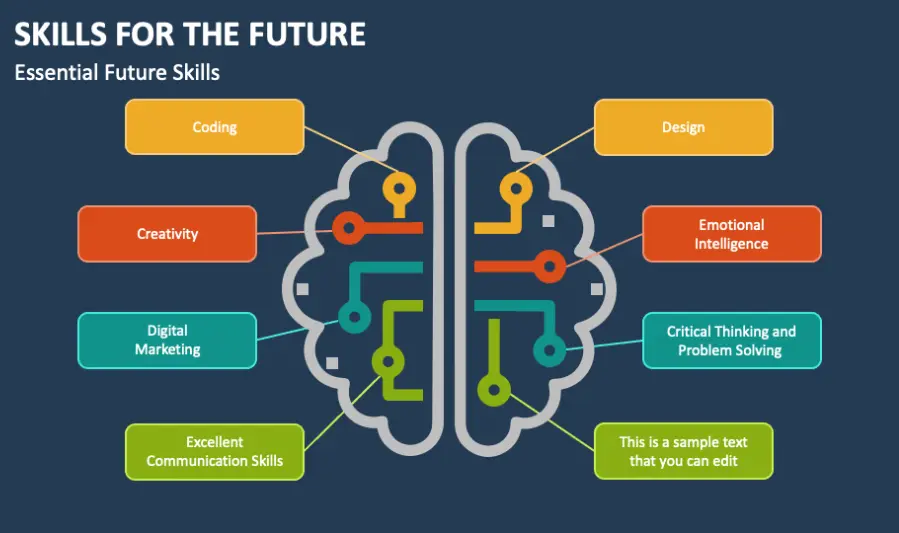
Future skills refer to the combination of abilities, knowledge, and attitudes that individuals need to thrive in the rapidly changing world of work and society. These skills go beyond technical expertise to include adaptability, creativity, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, digital literacy, and lifelong learning.
Difference Between Traditional Skills and Future Skills
Traditional skills often focus on specific, job-related tasks or knowledge that remain relatively stable over time, such as basic literacy, numeracy, and manual skills. Future skills, however, emphasize flexibility, problem-solving, collaboration, and continuous learning—qualities that prepare individuals to adapt to new technologies, complex challenges, and evolving work environments.
Why These Skills Are Crucial for the Evolving World
As automation and artificial intelligence reshape industries, many routine tasks are becoming automated, increasing the demand for uniquely human skills like creativity and empathy. Moreover, the global nature of work requires strong communication and intercultural collaboration. Future skills enable individuals to navigate uncertainty, innovate, and contribute meaningfully in a world that is constantly changing.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Explanation and Importance:
Critical thinking enables students to analyze information objectively, evaluate different perspectives, and make informed decisions. Problem-solving is about applying this thinking to find effective solutions to complex challenges.
Real-Life Applications:
From resolving conflicts in teamwork to tackling real-world issues like climate change, these skills help students navigate ambiguity and create practical solutions.
How to Practice:
Encourage activities such as debates, case studies, puzzles, and project-based learning that require analysis and reasoning.
B. Digital Literacy and Technology Skills
Overview:
Future learners need proficiency in digital tools, coding, data literacy, and an understanding of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence.
Role in Industries:
Technology is embedded across sectors—from healthcare and finance to manufacturing—making digital competence essential for nearly every career.
How to Gain Experience:
Students can engage in coding clubs, online courses, digital projects, and using data analysis tools to build hands-on skills.
C. Communication and Collaboration
Importance:
Effective communication is critical for sharing ideas clearly, listening actively, and building relationships. Collaboration skills enable students to work productively in diverse and virtual teams.
Enhancing These Skills:
Group projects, presentations, peer reviews, and participation in team sports or clubs foster strong communication and teamwork.
D. Adaptability and Resilience
Why It’s Essential:
With rapid technological and societal changes, students must adapt to new situations and recover from setbacks.
Developing a Growth Mindset:
Encourage viewing challenges as opportunities to learn rather than obstacles.
Building Resilience:
Teach stress management techniques, goal setting, and reflective practices to help students persevere through difficulties.
E. Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
Role:
These skills improve teamwork, leadership, and interpersonal relationships by helping students understand and manage their own emotions and relate to others.
Cultivation Methods:
Activities like role-playing, mindfulness exercises, and group discussions about feelings and perspectives enhance emotional intelligence.
F. Creativity and Innovation
Importance:
Creativity drives problem-solving and progress by inspiring new ideas and approaches.
Encouraging Creativity:
Provide opportunities for experimentation, open-ended projects, and brainstorming sessions that celebrate original thinking.
G. Lifelong Learning and Self-Motivation
Necessity:
Continuous learning is vital as industries evolve and new knowledge emerges.
Fostering Motivation and Curiosity:
Help students set personal learning goals, explore interests deeply, and develop self-directed study habits through mentorship and reflective activities.
Practical Activities
- Project-Based Learning: Engage in real-world projects that require planning, research, collaboration, and problem-solving. For example, creating a community garden or developing a school newsletter.
- Coding Clubs: Join or start coding clubs to build digital literacy and teamwork skills while working on programming challenges or app development.
- Debates and Discussions: Participate in debates to practice critical thinking, effective communication, and empathy by exploring different viewpoints.
Using Online Platforms and Resources
- Leverage platforms like Khan Academy, Coursera, Codecademy, or TED-Ed to learn new skills at your own pace.
- Use digital tools like Google Workspace or collaborative apps (e.g., Slack, Trello) to enhance teamwork and project management skills.
Volunteering and Internships
- Volunteer in local organizations or community projects to develop empathy, communication, and leadership skills.
- Seek internships or job shadowing opportunities to gain hands-on experience, adaptability, and exposure to real workplace environments.
Seeking Mentorship and Feedback
- Connect with teachers, professionals, or community leaders who can provide guidance, encouragement, and constructive feedback.
- Regularly reflect on your progress, set goals, and be open to learning from mistakes to build resilience and self-motivation.
The Role of Educators and Parents

Supporting Skill Development at School and Home
Educators and parents play a crucial role in nurturing future-ready skills. At school, teachers can design learning experiences that encourage critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, and digital literacy through interactive lessons and project-based activities. Parents can reinforce these skills at home by encouraging curiosity, supporting homework that challenges thinking, and fostering open communication.
Creating Environments That Encourage Growth and Exploration
Both educators and parents should cultivate safe, supportive environments where students feel comfortable taking risks, making mistakes, and learning from them. This includes promoting a growth mindset, providing resources and opportunities for exploration, and recognizing effort and progress rather than just outcomes. By doing so, they help students build confidence, resilience, and a lifelong love of learning.
you may also like to read these posts:
Comparing Group Study and Self Study: Benefits and Best Uses
Best Business Computers in 2025: Performance & Reliability
Powerful & Compact: Best Portable Mini PCs for Work
Exploring Various Budgeting Strategies to Take Control of Your Mone
Preparing Students: Future Skills They Will Need to Thrive
Future Outlook: Skills for Jobs That Don’t Exist Yet
Preparing Students for Unpredictable Careers
The rapid pace of technological innovation means many future jobs haven’t even been invented yet. Preparing students for these unknown careers requires focusing on transferable skills—like problem-solving, creativity, and digital literacy—that can be applied across a wide range of fields. This flexible foundation helps learners navigate and succeed in careers that evolve or emerge unexpectedly.
Importance of Versatility and Lifelong Adaptability
In a constantly changing job market, versatility is key. Students need to be adaptable, ready to learn new skills, and comfortable with change throughout their lives. Cultivating a mindset of lifelong learning and resilience ensures they can continuously update their knowledge, pivot when needed, and thrive no matter what the future holds.
Parents and Communities Supporting Future Skills Development
Creating Supportive Home Environments
Parents can foster future skills by providing a nurturing space where curiosity is encouraged, questions are welcomed, and learning is celebrated. This means offering opportunities for children to explore their interests, giving them time for creative play, and supporting their efforts without focusing solely on outcomes.
Encouraging Exploration and Failure as Learning Tools
It’s important for parents and communities to help children understand that failure is a natural part of learning and growth. Encouraging risk-taking, experimentation, and resilience helps students develop confidence and problem-solving skills. Celebrating effort and lessons learned from mistakes reinforces a growth mindset.
Community Programs and Resources for Skill-Building
Communities can support skill development by offering programs such as coding workshops, art classes, debate clubs, and volunteer opportunities. Libraries, youth centers, and local organizations often provide accessible resources and safe spaces for students to practice collaboration, leadership, and creativity outside the classroom.
Challenges and Barriers to Future Skills Development
Equity Issues and Access to Technology
Not all students have equal access to the devices, internet connectivity, or digital tools needed to develop essential future skills. This digital divide can widen existing educational inequalities, limiting opportunities for many learners, especially those from underserved or rural communities.
Curriculum Rigidity and Standardized Testing Pressures
Many education systems still prioritize traditional curricula and standardized testing, which often focus on memorization rather than critical thinking, creativity, or collaboration. This rigidity can restrict teachers’ ability to incorporate innovative, skill-focused learning approaches that prepare students for future challenges.
Teacher Preparedness and Professional Development Needs
Effective future skills development requires educators who are trained and confident in using modern teaching methods and technology. However, many teachers face gaps in professional development, limited resources, and high workloads, making it difficult to implement new approaches consistently and effectively.
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Skills
AI-Powered Personalized Learning and Tutoring
Artificial intelligence is transforming education by offering personalized learning experiences tailored to each student’s pace, style, and needs. AI tutors provide instant feedback and adapt content dynamically, helping learners master skills more effectively and efficiently.
Virtual and Augmented Reality for Immersive Education
VR and AR technologies create immersive, interactive environments that enhance understanding and engagement. From virtual science labs to historical simulations, these tools offer hands-on learning experiences that foster creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
Blockchain for Credentialing and Lifelong Learning Tracking
Blockchain technology enables secure, transparent tracking of skills and credentials over a lifetime. This allows learners to build verifiable portfolios of achievements and micro-credentials, supporting continuous education and career mobility in a rapidly changing job market.
Increased Focus on Mental Health and Well-Being as Foundational Skills
Recognizing the link between well-being and learning, schools are integrating mental health support and social-emotional learning into curricula. Building resilience, self-awareness, and stress management skills is becoming essential for students to succeed both academically and personally.
Faqs:
What are future skills, and why are they important for students?
Future skills are abilities that prepare students to thrive in a rapidly changing world, including critical thinking, digital literacy, and adaptability. They help students succeed in both their careers and personal lives.
How can students start developing future skills today?
Students can build future skills by engaging in project-based learning, practicing problem-solving, using technology tools, collaborating with peers, and seeking opportunities for continuous learning.
Are future skills only important for tech-related careers?
No, future skills like communication, emotional intelligence, and creativity are valuable across all industries and professions, not just in technology.
What role do parents and teachers play in developing future skills?
Parents and teachers support future skills development by encouraging curiosity, providing resources, fostering a growth mindset, and creating learning environments that promote exploration and resilience.
How will future skills help students with jobs that don’t exist yet?
Future skills equip students with adaptability and problem-solving abilities, allowing them to navigate and succeed in emerging careers and industries that may not even exist today.
Conclusion
As the world continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the skills students develop today will shape their success tomorrow. Future skills like critical thinking, digital literacy, adaptability, and emotional intelligence are essential tools that empower students to navigate uncertainty and seize new opportunities. By actively cultivating these skills through education, practice, and real-world experiences, students can prepare themselves not just for specific jobs, but for lifelong learning and growth in any career path they choose. Investing in these future skills today is an investment in a resilient, innovative, and adaptable generation ready to thrive in tomorrow’s world.